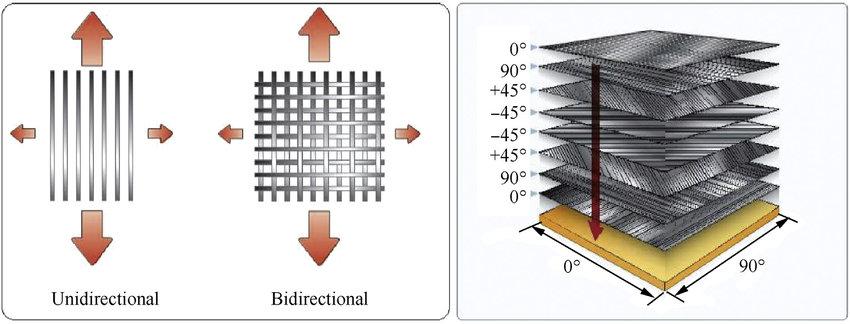
Definition
The direction in which the fibers in a composite material are aligned.
Importance
Determines the mechanical properties and strength of the composite.
Types
- Unidirectional: Fibers aligned in one direction; high strength in that direction.
- Bidirectional: Fibers aligned in two directions; balanced properties.
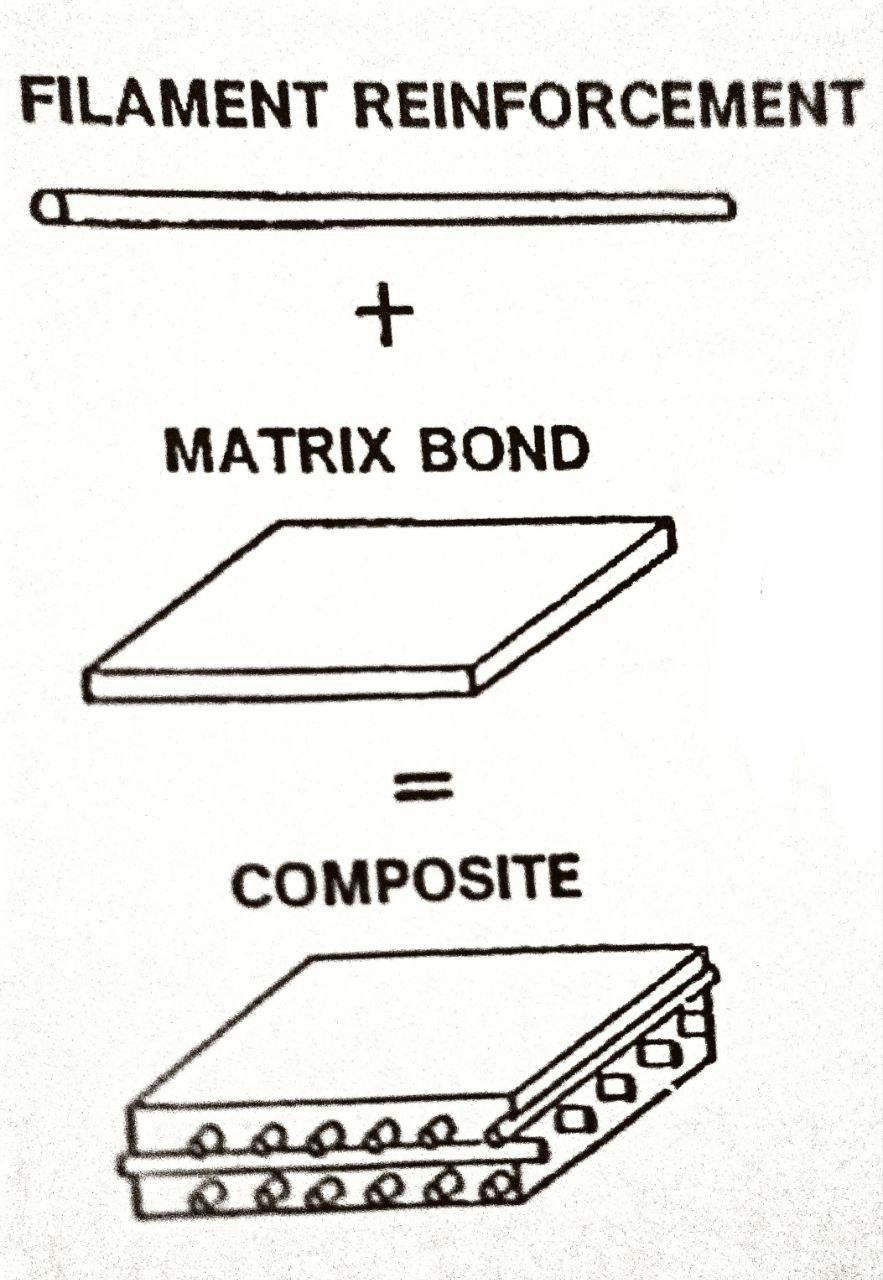
Composite Component Parts
Filament Reinforcement
Definition
Thin, strong fibers that provide strength and stiffness to composites.
Types
- Carbon Fibers: High strength and stiffness; lightweight.
- Glass Fibers: Good strength; more affordable.
- Aramid Fibers: High impact resistance; lightweight.
Applications
Aircraft structural components, such as wings and fuselage.
Matrix Bond
Definition
The material that surrounds and holds the filaments together.
Types
- Epoxy: High-performance resin with excellent mechanical properties.
- Polyester: More affordable, but lower performance.
- Phenolic: Good fire resistance.
Function
- Transfers loads between fibers.
- Provides shape and protects fibers.
- Enhances environmental resistance.
Composite
Definition
A material made from combining filament reinforcement and matrix bond.
Properties
- High strength-to-weight ratio.
- Customizable mechanical properties.
- Good fatigue and impact resistance.
Applications
Widely used in aircraft for structural parts, including wings, fuselage, and control surfaces.